Have you ever wondered about the gig economy and how it affects work? Well, I’m here to break it down for you in plain and simple terms.
The gig economy is all about people doing jobs as freelancers or independent workers.
Instead of having a regular job with one company, they work on specific projects or “gigs.”
This way of working has become more popular thanks to technology, which makes it easy for people to find jobs and get paid, even if they’re far away.
As the gig economy keeps growing, it’s likely that many of us will end up working this way.
Recent events like the COVID-19 pandemic have made this even more important to think about.
So, why should you care about the gig economy?
Well, it’s crucial to understand how it works because it might be the way you work in the future. Being ready and informed is the best way to prepare for this new way of working.

The Gig Economy: An Overview
The gig economy, also known as the freelance or on-demand economy, refers to a labor market characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work. It has grown substantially in recent years, revolutionizing traditional employment models.
This transformation is driven by several factors:
1. The Rise of Technology
Technological advancements, particularly the proliferation of smartphones and internet accessibility, have facilitated gig work. Online platforms like Uber, Upwork, and Airbnb have made it easier for individuals to offer services or rent out assets.
2. Flexibility and Autonomy
One of the key attractions of the gig economy is the flexibility it offers. Gig workers can choose their hours and projects, providing a level of autonomy that traditional employment often lacks.
3. Diverse Opportunities
The gig economy spans various sectors, including ride-sharing, freelancing, delivery services, and short-term rentals. This diversity creates opportunities for a wide range of skills and services.
What is the gig economy?
It’s understandable if you’re skeptical. Continue reading, and I’ll try to change your mind.
You’ve probably come across members of the gig economy. They have the same appearance as the rest of us.
For example, if you’ve ever used an Uber or a Bolt (Taxify), you’ve experienced the gig economy!.
Uber and Bolt enable drivers to earn money by accepting customers via an app and being paid for each ride.
They are paid on a per-gig basis rather than a fixed salary.
The same is true for online freelancers and even your neighbor who cuts your hair.
Is this a good thing or a bad thing?
The digital economy (gig economy) can be compared to zero-hours contracts in the worst-case scenario.
There is a significant risk that freelancers may end up working for a single company with all of the benefits that come with it, except for the stability and rights that come with a full-time job.
There’s also no obligation to work with a third party. Someone who cuts hair is technically a part of the gig economy, as previously stated.
When done correctly, the gig economy can also be quite liberating for professionals.
This is especially true when it comes to professional work done online. You can now choose which jobs you want to do to fit your work schedule around your lifestyle.
Assume you’re a data analyst, copywriter, developer, or information security, expert.
In the gig economy, working online would involve taking up freelancing projects with one or more employers and getting paid for each one.
This would allow you to work from home, choose the kinds of work that would benefit your career (or simply appeal to you), and determine your own schedule.
The Gig Economy: Impact on Traditional Employment
The rapid growth of the gig economy has had far-reaching implications for traditional employment models. While it has brought about positive changes, it has also raised concerns.
The Positives
- Increased Job Opportunities: The gig economy has created numerous job opportunities, allowing people to enter the workforce who may have otherwise struggled to find employment.
- Entrepreneurship: Gig workers often act as entrepreneurs, managing their businesses and building their brands. This fosters a sense of independence and self-reliance.
- Skill Development: The diverse nature of gig work encourages individuals to acquire a wide range of skills, which can be valuable for personal and professional growth.
The Concerns
- Lack of Job Security: Gig workers typically lack the job security and benefits associated with traditional employment, such as health insurance and retirement plans.
- Income Instability: Income in the gig economy can be unpredictable, as it depends on the availability of projects and clients. This instability can lead to financial stress for some.
- Regulatory Challenges: Many countries are still grappling with how to regulate the gig economy, leading to legal disputes and uncertainties.
Why is working online absolutely inevitable?
So, what is it about the gig economy that makes it inevitable?
Consider the perspective of an IT company in need of a web designer or a full stack developer.
This company has two options: employ local workers or utilize a platform like UpWork or Fiverr to hire a competent individual on a per-job basis.
In the first case, the firm must go through the time-consuming and costly process of interviewing and training a new employee. It must give office space, sick leave, and health insurance.
At the same time, the “pool” of local talent from which it may pick is strictly limited. This is especially true if a specific type of competent professional, such as a machine learning researcher, is required.
How many people do you believe are looking for jobs within a 50-mile radius of your current location?
In the latter, a business just pays for the labor it needs, and it may choose from a large group of candidates to select someone with the right skill set and expertise.
This is where the decision comes down to:
- Someone who isn’t the best match for the position and will cost a lot of money and time.
- Someone who is perfectly qualified for the position and has no strings attached.
Working with a distributed workforce is now not only possible, but also ideal, thanks to remote collaboration tools, project management systems, and remote collaboration.
We do precisely that at Jobs Tanzania: we have team members all around the country participating in our initiatives and discussing ideas and strategies. Countless tech startups do the same thing.
Is it possible that companies will continue to hire through traditional channels? How long before the typical office becomes redundant?
Those who fail to adapt will almost certainly be left behind.
Covid’s Impact
While the concept of an army of online freelancers has been on the horizon for some time, recent global events are likely to speed the process up.
Hundreds of millions of people throughout the world are now compelled to work from home.
Companies have had to react rapidly in order to put in place the required security and collaboration technologies.
Employees have also set up home offices, become used to not having to go to work every day, and eventually learned how to work quickly and efficiently without a manager hovering over them.
It’s no surprise that I’m hearing a lot of “not going back” whispers from my employed friends.
But here’s the thing: now that companies are used to not having their workers in the office, how long will it be before they learn they can hire from different parts of the world? Or not to hire at all?
What does the gig economy mean for you?
Does that make you feel uncomfortable? It doesn’t have to be that way!
Not only do companies have a strong opportunity to transition to this new gig economy model; the rest of us may gain as well.
Sure, there’s less job security, but there’s also no income limitation, and you’ll get to keep a bigger piece of the pie.
Working remotely and on a per-gig basis, on the other hand, allows you to work around your ideal lifestyle. Consider how much time you waste every day getting to and from work.
Many people might save hundreds of hours on travel each year even if they worked the same hours.
You’ll be able to take days off whenever it’s appropriate for you, and you’ll be able to manage your working hours as desired.
Monday through Thursday, you might work an extra two hours and have Friday off.
This is referred to as “lifestyle design,” which is arranging your work around your life rather than vice versa.
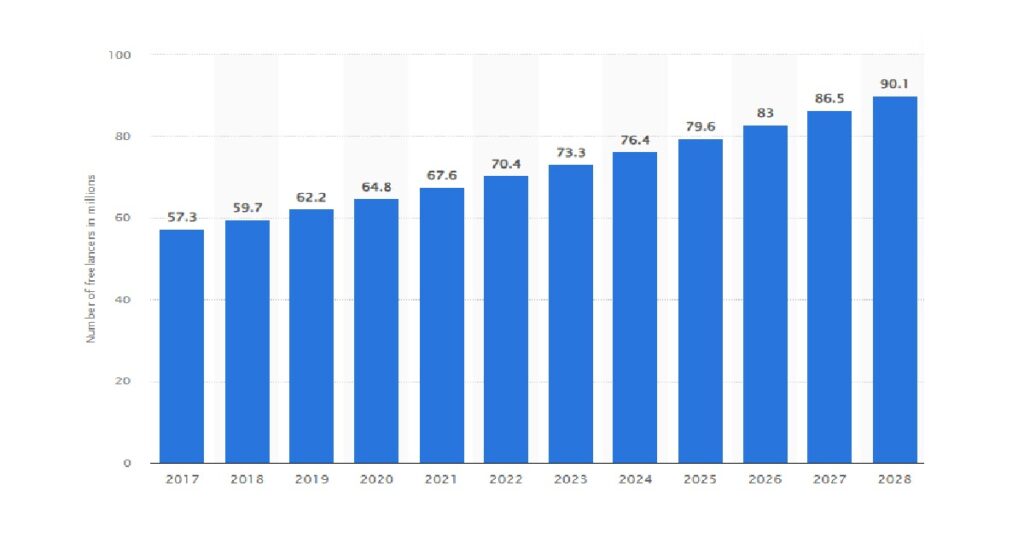
Gig economy statistics
The top five most essential gig economy statistics:
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the gig economy?
The gig economy is a labor market characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, facilitated by online platforms.
How big is the gig economy?
Approximately 34% of the U.S. workforce participates in the gig economy, and it continues to grow.
What are the benefits of gig work for employers?
Employers benefit from a flexible workforce, cost savings, and access to a diverse talent pool.
What challenges do gig workers face?
Gig workers often lack job security, benefits, and face income instability due to fluctuating demand.
What is the likely future of work in the gig economy?
The future may involve hybrid work models, skill enhancement, and increased regulation to protect gig workers.
How can individuals prepare for the gig economy’s future?
Staying adaptable, upskilling, and being open to diverse work opportunities are key to success in the gig economy.
Conclusion:
As the gig economy continues to shape the way we work, it’s crucial to stay informed and prepared for the changes it brings. Embracing flexibility, enhancing skills, and advocating for worker rights will be essential steps in navigating the evolving landscape of employment.
Keep an eye on Kidigitali.com for more information on how to accomplish this and how to prepare for the exciting new future!
We’ll look at how to make the most of the new gig economy, as well as how to prepare for jobs that will be in great demand in the future decades.
In conclusion, “Learning about the gig economy and the likely future of work” is not just a choice but a necessity in today’s world of work.
